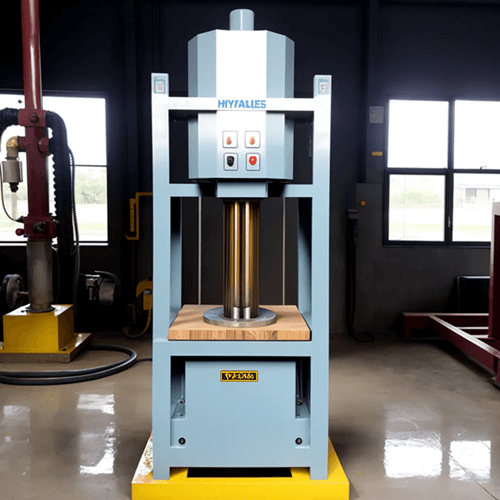
Hydraulic cylinders generate high force and pressure to operate a hydraulic press, which is a powerful machine utilized in various industries that require high force or pressure for specific tasks. The machine operates based on Pascal’s law, which states that an enclosed fluid transmits pressure equally to every part of the fluid and the container walls. This principle allows a small force applied to a small piston to be amplified and exerted as a larger force on a larger piston.
Origin of the Hydraulic Press
Joseph Bramah, an English engineer and inventor, invented the hydraulic press in 1795. The operation of a hydraulic press is based on Bramah’s principle, also known as Pascal’s principle. According to this principle, applying pressure at one point in an enclosed, incompressible fluid transmits the pressure equally in all directions throughout the fluid, enabling the multiplication of force.
Working Mechanism of Hydraulic Presses
The operation of a hydraulic press is relatively straightforward, involving two cylinders connected by a pipe. The cylinders vary in size, with one being larger than the other. When force is applied to the smaller cylinder, it creates pressure that is transmitted through the fluid in the pipe to the larger cylinder. Due to the difference in surface area, the larger cylinder generates a greater force than the one applied initially, thus amplifying the force.
Industrial Applications of Hydraulic Presses
Hydraulic presses are remarkably versatile, finding applications in a myriad of industrial sectors.
- Manufacturing Industry: The manufacturing sector employs hydraulic presses for various tasks, including stamping, forging, molding, and deep drawing. These presses shape metal into different forms, such as car parts, kitchen utensils, and airplane parts. Additionally, companies use hydraulic presses in the production of medical equipment and electrical parts.
- Construction Industry: Hydraulic presses also play a significant role in the construction industry. They are used to make bricks, tiles, and concrete blocks. Their power and efficiency make them ideal for creating large quantities of construction materials quickly.
- Automotive Industry: The automotive sector uses hydraulic presses for various tasks, including straightening, stamping, punching, and bending metal sheets into different shapes to manufacture vehicle bodies and other parts.
- Plastic Industry: The plastic industry utilizes hydraulic presses for compression molding, a process that involves placing heated raw material into the press and applying force until the material cools and solidifies into the desired shape.
- other industries and applications:In jewelry making, hydraulic presses can form metal into various shapes like rings and bracelets. In agriculture, hydraulic presses are useful for pressing and baling hay. The aerospace industry also utilizes hydraulic presses for forming and shaping composite materials.
Advantages of Hydraulic Presses
Hydraulic presses offer several benefits when compared to other types of presses:
- Power: The most significant advantage of a hydraulic press is its power. The hydraulic fluid’s incompressibility allows the press to exert a substantial amount of pressure, enabling it to handle heavy-duty tasks efficiently.
- Versatility: Hydraulic presses can function with various materials, including metal, wood, and plastic, making them highly versatile in an industrial context.
- Precision: Hydraulic presses offer excellent precision and control. The hydraulic press can adjust the pressure to match the specific requirements of the task at hand, ensuring that the output meets the desired specifications.
- Durability: Hydraulic presses are robust and durable, capable of withstanding heavy use over extended periods.
Limitations and Safety Concerns
Despite their many advantages, hydraulic presses do have some limitations. They are slower in operation than mechanical presses and require more maintenance due to potential hydraulic fluid leaks. Additionally, they consume more energy and are more expensive upfront.
there are also some disadvantages to hydraulic presses. One of the main disadvantages is their high initial cost, which can make them prohibitively expensive for some businesses. In addition, hydraulic presses can be relatively slow to operate compared to other types of machines, which can limit their usefulness in certain applications.
Safety is a paramount concern when operating hydraulic presses. Operators must always wear appropriate protective gear while operating the machines, and they should regularly inspect and maintain the hydraulic presses to prevent accidents.
Conclusion
From their invention in the 18th century to their widespread use in various industries today, hydraulic presses have proven to be valuable tools. With their power, versatility, and precision, they have facilitated advancements in manufacturing, construction, automotive, and plastic industries. Despite some limitations and safety concerns, their benefits far outweigh the drawbacks, making them an indispensable part of the industrial landscape.